The Accuracy of IoT Devices in Asthma Monitoring: A Deep Dive
delving into how accurate IoT devices are in monitoring asthma conditions and their reliability compared to traditional methods.
The Accuracy of IoT Devices in Asthma Monitoring: A Deep Dive
Posted by Dr. Oliver Williams, reviewed by Dr. Helena Rodriguez | 2024-Mar-21
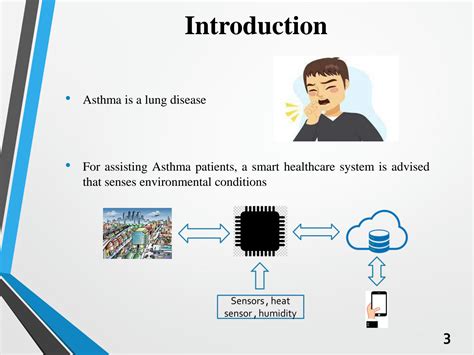
Asthma, a chronic respiratory condition affecting millions worldwide, has seen a remarkable shift in management strategies in recent years. With the advent of Internet of Things (IoT) technology, the landscape of asthma monitoring has been transformed, offering new avenues for patients to track and manage their symptoms. But how accurate are these IoT devices, and how do they compare to traditional monitoring methods? Let's dive deep into this intriguing topic.
At the core of this discussion lies the inherent complexity of asthma, a condition characterized by inflammation and constriction of the airways. Traditionally, healthcare professionals have relied on a combination of patient-reported symptoms, lung function tests, and physical examinations to assess asthma severity and guide treatment. However, these conventional methods can be subjective and may not capture the nuances of an individual's asthma experience.
Enter IoT devices, which promise to revolutionize asthma monitoring by providing a more comprehensive and objective assessment. These smart devices, ranging from wearable sensors to smartphone-connected inhalers, are designed to continuously track various parameters, such as respiratory rate, peak flow, and medication usage. By leveraging advanced algorithms and machine learning, these IoT solutions aim to provide patients and healthcare providers with real-time insights into the state of an individual's asthma.
But the crucial question remains: how accurate are these IoT devices in capturing the true picture of asthma? Recent studies have shed light on this matter, with mixed results. Some research has shown that IoT devices can effectively detect asthma exacerbations and provide reliable data on lung function, often outperforming traditional methods. For instance, a study published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology found that a wearable sensor was able to accurately predict asthma attacks with a sensitivity of 80% and a specificity of 76%.
However, other studies have highlighted the limitations of IoT devices in asthma monitoring. Factors such as environmental conditions, user error, and individual physiological differences can impact the accuracy of these devices, leading to inconsistent or even misleading results. A review in the Annals of the American Thoracic Society cautioned that while IoT devices show promise, more research is needed to establish their reliability and clinical utility.
As with any emerging technology, the accuracy and reliability of IoT devices in asthma monitoring are still evolving. Healthcare professionals and patients must approach these tools with a critical eye, recognizing their potential while also acknowledging their limitations. Careful integration of IoT data with traditional monitoring methods, along with ongoing validation and refinement of these devices, will be crucial in ensuring accurate and effective asthma management.
As the field of IoT-enabled asthma monitoring continues to advance, the question of accuracy remains a topic of active research and discussion. What are your thoughts on the role of IoT devices in managing this complex condition? Share your insights and experiences in the comments below.
User comments
More Topics to Explore
Can IoT Devices Revolutionize Asthma Care?
Discussing how the integration of IoT devices can potentially transform asthma care and management, exploring benefits and possible limitations.
Smart Inhalers: Gimmick or Game-Changer for Asthmatics?
A look into smart inhalers, their functionality, and whether they significantly improve asthma management or are just a tech fad.
How Reliable Are Wearable Devices in Monitoring Asthma Symptoms?
Examining the reliability and efficacy of wearable devices in tracking and managing asthma symptoms.
IoT and Asthma: Reducing Hospital Visits?
Discussing if IoT devices can help in reducing the number of hospital visits for asthma patients by providing better at-home management tools.
Privacy Concerns with IoT Asthma Management Tools
Addressing privacy issues related to using IoT devices for asthma management and ways to protect sensitive health data.
Integration Challenges of IoT Devices in Existing Asthma Care Protocols
Exploring the challenges healthcare providers face when integrating IoT devices into existing asthma care protocols.
Empowering Asthma Patients Through IoT: Real Patient Stories
Sharing success stories of asthma patients who have significantly benefited from using IoT devices in their management plan.
Are IoT Asthma Management Solutions Cost-Effective?
Analyzing the cost-effectiveness of IoT-based asthma management solutions compared to conventional treatment methods.
Customizing IoT Devices for Individual Asthma Plans: How Far Can We Go?
Discussing the potential for customizing IoT devices to fit individual asthma management plans and the technical limitations.
Predictive Analytics in IoT Devices: A Future for Asthma Prevention?
Exploring how predictive analytics in IoT devices could help in forecasting asthma attacks and preventing severe episodes.
Challenges in Adopting IoT Solutions for Asthma in Low-Income Areas
Addressing the challenges and barriers to adopting IoT solutions for asthma management in economically disadvantaged areas.
The Role of IoT in Pediatric Asthma Management
Examining the impact and potential of IoT devices in managing asthma among children and enhancing their quality of life.
Interoperability of IoT Asthma Devices with Healthcare Systems
Discussing the importance and challenges of IoT asthma devices' interoperability with existing healthcare systems and electronic health records.
The Environmental Impact of Using IoT Devices for Asthma
Considering the environmental implications of widespread IoT device use in asthma management and sustainable alternatives.