Daily Use of Bronchodilators: Benefits vs. Risks?
Weigh the benefits against the risks of using bronchodilators on a daily basis for asthma management.
Daily Use of Bronchodilators: Benefits vs. Risks?
Posted by Dr. Oliver Williams, reviewed by Dr. Helena Rodriguez | 2024-Apr-04
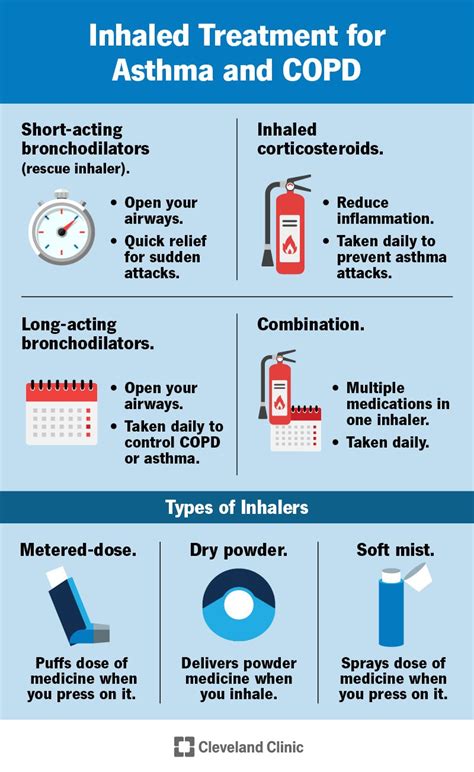
For individuals living with asthma, the daily use of bronchodilators has long been a topic of discussion and debate. Bronchodilators are a class of medications designed to relax and open the airways, providing relief from the symptoms of asthma, such as wheezing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. However, the decision to use these drugs on a daily basis is a delicate balance, as both benefits and risks must be carefully considered.
On the benefit side, regular use of bronchodilators can effectively manage the underlying inflammation and constriction of the airways that characterize asthma. By keeping the airways open and allowing for easier breathing, these medications can significantly improve a patient's quality of life, reduce the frequency and severity of asthma attacks, and minimize the need for emergency interventions. Numerous studies have demonstrated the efficacy of daily bronchodilator use in improving lung function, reducing symptom burden, and enhancing overall asthma control.
Furthermore, the timely use of bronchodilators can prevent the progression of asthma and potentially reduce the risk of long-term lung damage. By maintaining optimal airflow, these medications may help to preserve lung function and prevent the development of irreversible airway remodeling, a common complication of uncontrolled asthma.
However, the potential risks associated with the daily use of bronchodilators must also be taken into account. Overreliance on these medications, particularly without the concurrent use of anti-inflammatory therapies, can lead to a phenomenon known as "beta-agonist tolerance." This condition can reduce the effectiveness of bronchodilators over time, potentially increasing the risk of asthma exacerbations and compromising overall disease management.
Additionally, the regular use of short-acting bronchodilators, such as albuterol, has been linked to an increased risk of adverse cardiovascular events, including heart palpitations, elevated blood pressure, and even myocardial infarction in some cases. These risks may be amplified in individuals with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions or other comorbidities.
Ultimately, the decision to use bronchodilators on a daily basis should be made in close consultation with a healthcare provider, taking into account the individual's asthma severity, symptom patterns, and overall health status. The goal should be to strike a balance between effectively managing asthma symptoms and minimizing the potential for long-term complications or adverse effects.
For many patients, the daily use of bronchodilators may be necessary and beneficial, particularly when combined with anti-inflammatory medications and a comprehensive asthma management plan. However, for others, a more tailored approach, involving the intermittent use of bronchodilators or the exploration of alternative treatment options, may be more appropriate.
As the medical community continues to enhance our understanding of asthma management, the debate surrounding the daily use of bronchodilators will undoubtedly evolve. Patients and healthcare providers must remain vigilant, carefully weighing the benefits and risks, and working together to develop a personalized approach that optimizes disease control and minimizes potential harm.
What are your experiences with the daily use of bronchodilators for asthma management? We'd love to hear your perspective on the benefits and risks involved.
User comments
More Topics to Explore
Are Bronchodilators a Quick Fix or Permanent Relief for Asthma?
Explore the distinction between the immediate relief bronchodilators provide and their role in long-term asthma management.
Bronchodilators vs. Inhaled Steroids: Which is Better for Long-term Asthma Control?
Dive into the debate on the effectiveness of bronchodilators compared to inhaled steroids for managing asthma in the long run.
Can Overuse of Bronchodilators Worsen Asthma Symptoms?
Discuss how excessive use of bronchodilators might counterintuitively lead to worsening asthma symptoms.
Bronchodilators: Emergency Relief or Everyday Use?
Debate whether bronchodilators should be reserved for emergency asthma attacks or used regularly as part of daily treatment.
How Do Long-acting Bronchodilators Fit into Asthma Treatment Plans?
Delve into the role and effectiveness of long-acting bronchodilators within comprehensive asthma treatment strategies.
Short-acting vs. Long-acting Bronchodilators: Pros and Cons?
Compare the advantages and disadvantages of short-acting and long-acting bronchodilators for asthma patients.
Bronchodilators' Side Effects: What Should Asthma Patients Be Aware Of?
Highlight the potential side effects of bronchodilators that asthma patients should be mindful of.
Combination Therapies with Bronchodilators: Yay or Nay?
Discuss the effectiveness and safety of combining bronchodilators with other asthma medications for treatment.
Bronchodilators in Pediatric Asthma: Safe or Risky?
Debate the safety and efficacy of bronchodilators for treating asthma in children.
Innovations in Bronchodilator Treatments: What's New?
Explore the latest advancements and innovative treatments in the realm of bronchodilators for asthma.
Bronchodilators and Exercise-Induced Asthma: A Perfect Match?
Delve into the effectiveness of bronchodilators in managing exercise-induced asthma.
Natural Alternatives to Bronchodilators: Do They Work?
Discuss the efficacy and safety of natural alternatives to bronchodilators in asthma treatment.
Bronchodilators and Allergy-Induced Asthma: The Connection?
Investigate how bronchodilators impact allergy-induced asthma and their role in treatment.
Bronchodilators in Asthma: How Personal Experiences Shape Treatment Choices?
Share and discuss how personal experiences with bronchodilators influence treatment decisions among asthma patients.